HEMATOLOGICAL DISEASES
DISEASE : LEUKEMIA
Definition
- Leukemia is cancer of body's blood forming tissues , including the marrow and the lymphatic system.
- Leukemia usually involves the white blood cells your white blood cells are potent infection fighters. They normally grow and divide in an orderly way , as your body needs them but in people with leukemia , the bone marrow produces abnormal white blood cells , which don't function properly.
Symptoms
Fever or chills
Persistent fatigue , weakness
Frequent or severe infections
Losing weight without trying
Swollen lymph nodes , enlargement of liver or spleen
Easy bleeding or bruising
Recurrent nosebleeds
Tiny red spots in skin
Excessive sweating ( especially at night )
Bone pain or tenderness
Classification
- Leukaemia can be broadly classified according to the cell of origin and their clinical course :
1) Acute Leukaemias
- Acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- Acute myeloid leukemia
2) Chronic Leukaemias
- Chronic lymphocytic leukemia
- Chronic myeloid leukemia
Acute Leukemia
- The acute leukaemias are stem cell disorders characterized by a malignant neoplastic proliferation and accumulation of immature hematopoietic cells in the bone marrow
- In acute leukemia , proliferation of cells which do not mature and leads to an increasing accumulation of useless cells which take up more and more marrow space at the expense of the normal haemopoietic elements.
- Eventually , this proliferation spills into the blood stream.
Classification of acute leukemia
A) Acute myeloid leukemia
B) Acute lymphoblastic leukemia
Clinical Features
Features of anaemia
- effort intolerance
- fatigue
- palpitation
- tachycardia
- pallor
- systolic flow murmur
Features of infection
- fever
- sore throat
- mouth ulcers
- pneumonia
Bleeding manifestations
- gum bleeding
- bruises
- petechiae
- fundal haemorrhage
Lymphadenopathy
Splenomegaly
Hepatomegaly
Bone tenderness
Gum hypertrophy
Investigation
✓ Blood Count
* Haemoglobin
* WBC count
* Platelets
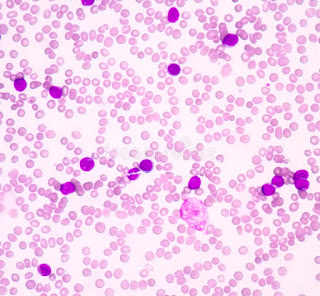
✓ Peripheral smears
* Blast cells and other primitive cells
✓ Bone marrow examination
* Hyper cellular with blast cells (20%)
* Presence of Auer rods in cytoplasm of blast cells
* Myeloid : erythroid ratio increased
* Erythropoiesis : decreased
* Megakaryocytes: reduced or absence
✓ Other Investigations
* Haemostatic function
* Renal function test
* Liver function test
* Serum LDH , Uric
Treatment
1) Induction phase
- induce remission immediately
* Vincristine , steroid
* Probably Anthracyclines
* It is about 4-6 weeks long
2) Consolidation phase
- eleminate residual sub-microscopic cancer cells
* Multiple treatment regimens based on patient's risk factors
* Cyclophosphamide , cytarabine
* Probably with interial maintenance phase and reinduction
* It is about 6-9 months long
3) Maintenance phase
- decrease relapse risk post-treatment.
* 6-MP and methotrexate
* Probably occasional pulses of cartiscosteroides and vincristine
- It is about 2-3 years long.
DISEASE LYMPHOMA.
- Lymphoma is a cancer of the lymphatic system , the body's disease-fighting network.
- The lymphatic system includes lymph nodes , spleen , thymus gland and bone marrow. lymphoma can affect all those areas as well as other organs throughout the body.
Types of lymphoma:
1) Hodgkin's lymphoma
2( Non- Hodgkin's lymphoma
1) Hodgkin's lymphoma
It is a cancer of the lymphatic system , which is part of immune system.
Pathological classification of Hodgkin's lymphoma:
A. Lymphocytic predominant
B. Nodular sclerosing
C. Mixed cellularity
D. Lymphocyte depleted
Clinical Features
✓ Lymphadenopathy
- enlarged , painless , rubbery , non tender lymph node , more often single axial group of lymph node are involved.
✓ Persistent fatigue
✓ Fever and chills
✓ Night sweats
✓ Unexpected body weight loss ( 10%)
✓ Loss of appetite
✓ Itching
Clinical staging ( Ann Arbor classification )
Stage I : involvement of one lymphatic group
Stage II : involvement of two lymphatic group on the same side of the diaphragm.
Stage III : involvement of lymphatic group on both side of diaphragm
Stage IV : widespread disease with involvement of diffuse extra lymphatic sites such as the bone marrow or liver.
A: Non systemic symptoms
B: with systemic symptoms
( Note: This clinical staging is same for both Hodgkin's lymphoma and Non- Hodgkin's lymphoma )
Investigation
- Lymph node biopsy
- Haemoglobin estimation reduced
- Total WBC count : raised
- Peripheral blood smear
- ESR:raised
- Serum LDH : raised
- Serum uric acid : raised
- For staging
* Chest x-ray
* USG for liver , spleen , lymph node
* CT scan : chest , abdomen
* Liver function test
* Renal function test
* Bone marrow , spleen , liver biopsy
* Staging laparotomy
Management
1. Radiotherapy
Indications:
- Stage I ( without systemic symptoms )
- Stage II ( without systemic symptoms)
- To lesions causing serious pressure problem
2. Chemotherapy
Indications:
-All patients with B symptoms
- Stage III
- Stage IV
Most effective combination of chemotherapy regimens:
ABVD: Adriamycin , Bleomycin , Vinblastine , Decarbazine
MOPP : Mustin , Oncovin , Prednisolone , Procarbazine.
2. Non- Hodgkin's lymphoma
- The neoplastic transformation of both( Bitta and T ) lymphatic cells with absence of the Reed-sternberg cell on histology is called Non- Hodgkin's lymphoma.
Causes
- Infection
- Genetics
- Immunology ( lymphoma occurs in congenital immunodeficiency states and in immunosuppressed and post organ transplantation patient.
Classification of NHL ( Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma)
- Low grade
- Intermediate grade
- High grade
Clinical Features
✓ Lymphadenopathy : enlarged, painless , rubbery , non-erythematous , non tender lymph nodes.
✓ B symptoms
- drenching night sweat
- 10% weight loss over 6 months
- fever
✓ Extra nodal involvement
✓ Hepatosplenomegaly
Investigation
Same as Hodgkin's lymphoma
Routine bone marrow examination
HIV test
Immunophenotyping of surface antigen to differentiate B or T cells
Management
✓ Radiotherapy
✓ Chemotherapy
( Chemotherapy regimens
CHOP : Cyclophosphamide , Doxorubicin , Vincristine , Prednisolone)
A. Low grade NHL
- Asymptomatic
- Not require therapy
Indications for treatment:
Mark systemic symptoms
Lymphadenopathy
Bone marrow failure
Treatment modalities
* Radiotherapy
* Chemotherapy
* Monoclonal antibody therapy
* Autologous stem cell transplantation
B. High grade NHL
- All patient need treatment at initial presentation
Treatment modalities:
* Radiotherapy
* Chemotherapy
* Monoclonal antibody therapy
* Autologous stem cell transplantation










Post a Comment
If you have any doubts please let us know .